Sometimes, when we make major life decisions, they do not always go as planned. One day, you graduate with a degree in marketing, but end up working professionally as a chef decades later, realizing that a path in corporate just wasn’t for you. It occurs more commonly than you think.
Many switch careers later on in life for various reasons. Some change their career path when they no longer feel fulfilled in their day-to-day lives, while others are hit with the sobering reality that the field they chose may not be as well-compensated as other, more lucrative careers.
Such is the reality for a lot of the working class. One of the more popular career shifts today is a shift to a career in tech. It’s a fast-growing field, and as a result, the opportunities for growth are plentiful, in terms of the roles and compensation.
{{ advertisement }}
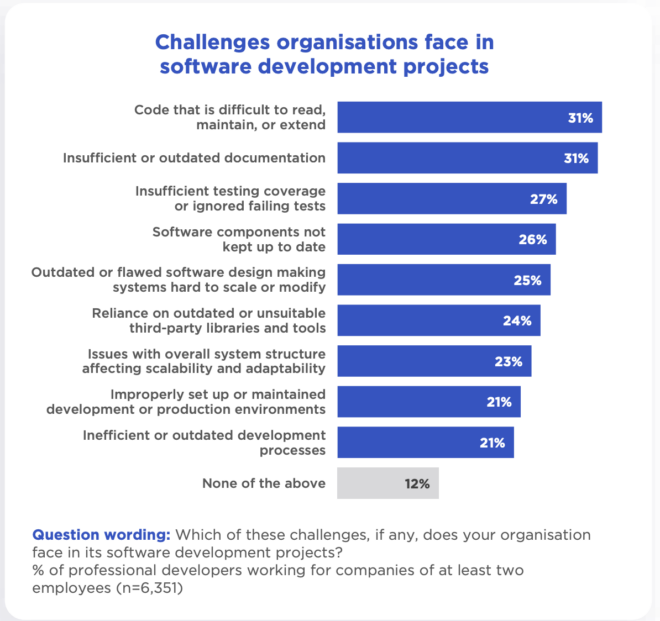
Hence, it’s no surprise that many are making the shift to tech today. The explosion of bootcamps, online courses, and affordable learning platforms has made skills more accessible, but it’s also led to an oversupply of entry-level talent. That’s why the dream of finding a job in tech today is a lot harder than it was five years ago.
Is making the switch to tech still possible in today’s job market? Absolutely. All it takes is finding the right learning path.
1. Assess Your Transferable Skills
Before zeroing in on coding tutorials or signing up for an expensive bootcamp, take note of the skills you already have. Some soft skills and hard skills are transferable, even if you didn’t come from a tech background yourself:
- Project management experience in another industry can still be useful in project management, product management, or tech operations roles.
- Data handling and analysis from finance or research work translates well into data science or analytics.
- Communication and collaboration skills are vital for client-facing roles like solutions engineering or UX research.
By already knowing what’s in demand in tech, you can shorten your learning curve and avoid wasting time on unrelated topics.
2. Identify Your Target Role
You might think that casting a wide net might make you more likely to find a job in tech, but it’s quite the opposite. Jumping in without a clear goal can lead to scattered learning that doesn’t prepare you for any specific job.
Take your time to research a career path in tech that well suits your skill set. For example, software engineering, UX design, data analysis, or cybersecurity. Look into the daily responsibilities of these roles, tools commonly and hiring requirements.
This research phase doesn’t need to take months, but it helps in narrowing your focus. A targeted approach will save you time and ensure the projects you work on are relevant to your future applications.
3. Choose the Right Learning Format
Once you figure out the best role for you, you can move forward and learn the necessary skills. Some people thrive in self-paced online courses that allow flexibility, while others do better in structured bootcamps with fixed schedules.
If you work best with structure and accountability, academic-style coaching—though often designed for younger students—can be just as effective for adult learners.
Its core principles of personalized learning, mentorship, and structured support adapt well to helping you build targeted skills based on your goals, background, and available time.
With the right coach, you get feedback, encouragement, and help avoiding common pitfalls—something especially valuable when transitioning to a tech career.
4. Build a Practical Portfolio
In tech, you increase your chances of landing a job if you have a portfolio, as it serves as proof. Employers want to see that you can apply what you’ve learned, not just that you’ve completed a course.
A strong portfolio features projects that solve real-world problems and use tools recognized by the industry.
Don’t wait until you’ve completed a course or certification program before you start building. It’s better to create smaller projects as you go and improve them over time. This way, you have tangible results to show recruiters even before your learning is complete.
5. Stay Current With Industry Trends
Technology moves fast, and so much so that the trendiest framework today might be outdated in a few years. If you don’t stay up to date and frequently upskill, then you will get left behind.
Make it a habit to read tech news, subscribe to industry newsletters, and follow leaders in your chosen field.
Participating in open-source projects can also expose you to new tools and practices before they hit the mainstream. Staying current helps you remain competitive long after you land your first role.
Final Thoughts
Though these are all useful steps in switching to a career in tech, remember that it’s also about the mindset. You have to stay persistent, adapt easily to new changes, and keep the willingness to learn alive. Couple that with the five steps above, and a career shift to tech will be highly achievable.